🦠COVID🦠
🌍 🦠
Global COVID cases continue to rocket back upward. According to the latest weekly infection assessment from the World Health Organization, there were over 1.4 million new coronavirus infections around the world (+63%) in the latest 28-day reporting period ending August 13. Over 2,300 more lives were also lost (-56%).
South Korea is the epicenter of this latest infection surge as it reported more than 1.2 million new COVID cases (+140%) and 340 more virus deaths (+91%). Infection numbers also rose in Italy (+10%) and the United Kingdom (+60%). Other COVID hot spots include Afghanistan and Iran.
Keep in mind that all of these numbers are very likely underreported.
Several countries are recording an increase in COVID deaths including the Philippines with 162 fatalities (+5300%). The others are Portugal (+7%), Bangladesh (+71%), and Iran (+15%).
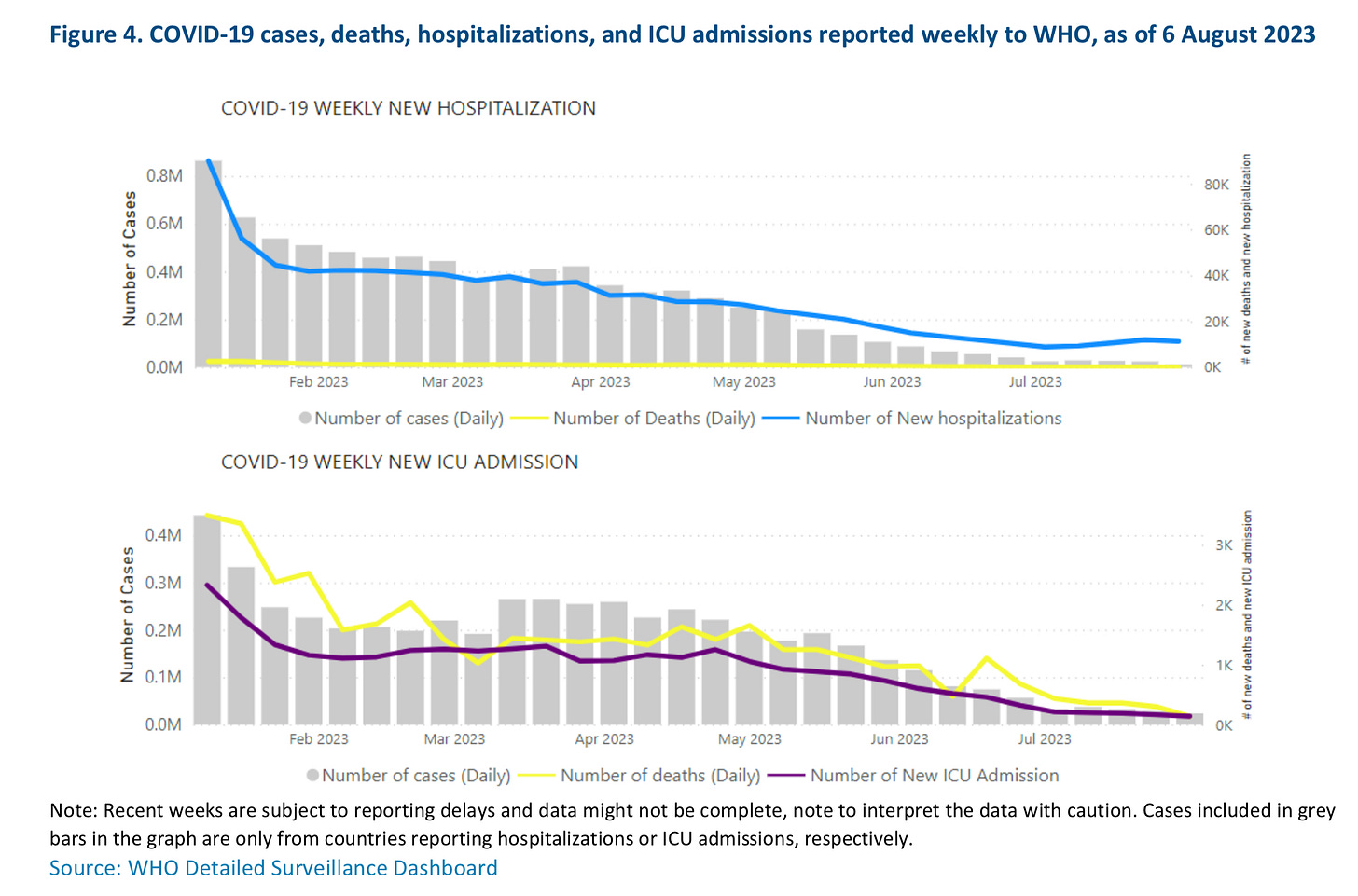
Just 26 countries are reporting hospitalization data to the WHO. Of those, there were 43,193 new admissions (-3%). Of the 23 nations reporting intensive care numbers, there were 654 new patients (-55%).
With over 32,000 new admissions (+32%) the United States had the most COVID hospitalizations of the countries reporting such data. Other countries seeing significant increases in hospital admissions include Bangladesh (+669%), Kyrgyzstan (+150%), Greece (+62%), Malta (+45%), and Mexico (+27%).
Just two countries are reporting significant new ICU admissions. They are Greece (+30%) and Latvia (+200%).
🇪🇺
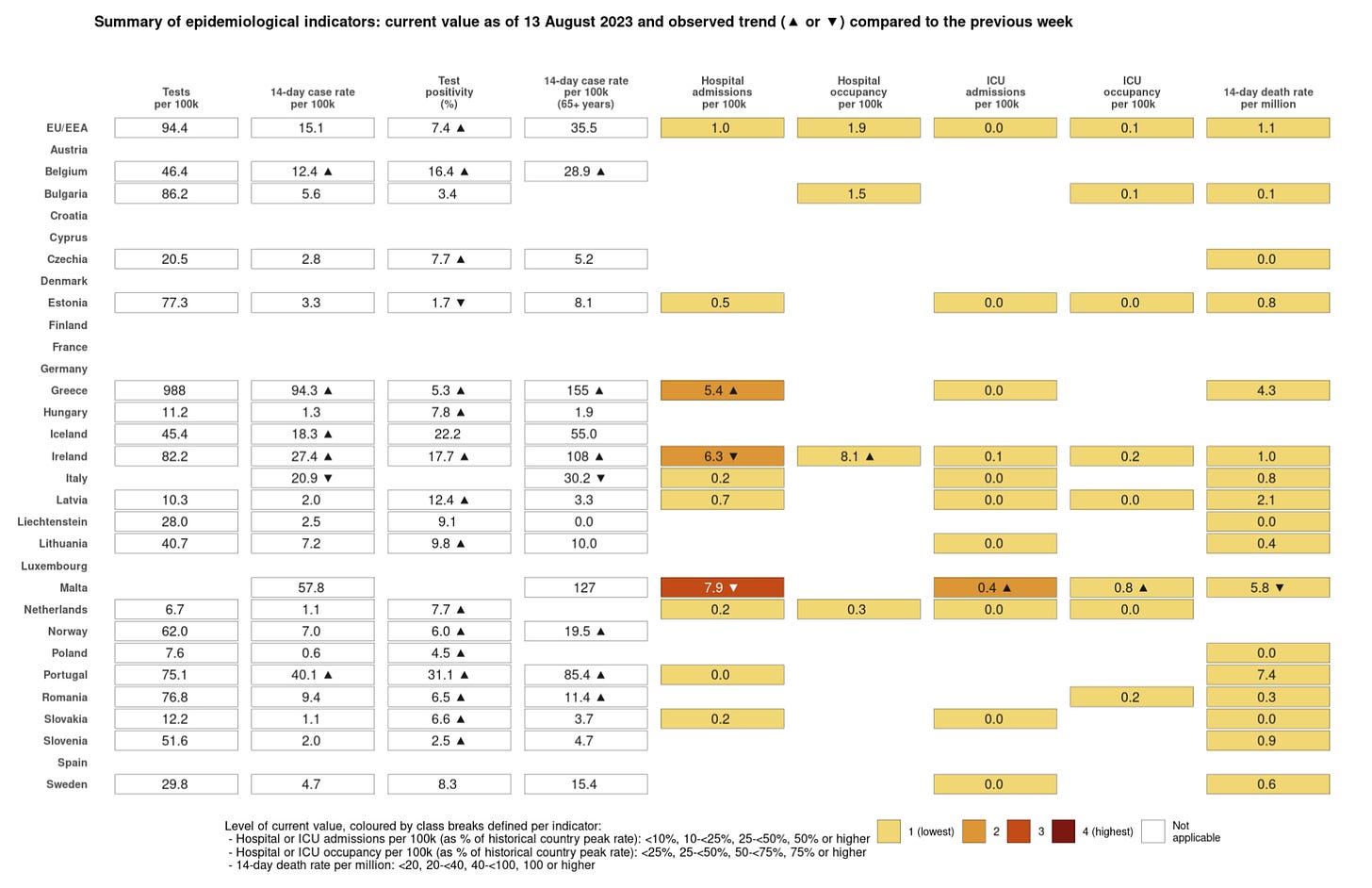
In its latest COVID snapshot, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control warns that based on available data there is evidence of increasing coronavirus spread across some European countries. But it also cautions that due to fewer countries reporting infection data and lackluster testing, it is “increasingly challenging” to get a handle on the true picture.
Just four counties across Europe registered “sufficient testing data” to provide even a small glimpse into the infection situation.
Three countries reported a rise in the number of infection-related hospitalizations. Greece is seeing hospital admissions increase. Hospital occupancy is up in Ireland. Malta is the only country to report an increase in severe cases requiring intensive care.
Four countries reported that COVID cases were increasing across all age groups (Belgium, Greece, Ireland, and Portugal). One (Iceland) saw rising case numbers but just among those under the age of 65. Two others (Norway and Romania) are also seeing rising infections but just among vulnerable seniors over 65.
Test positivity, the percentage of positive tests per testing volume, has increased at the EU level and among a whopping 14 individual countries.
No country reported an increase in fatalities.
Nine countries, including some of the biggest in Europe, didn’t report any COVID data at all. They are Austria, Croatia, Cypress, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Luxembourg, and Spain.
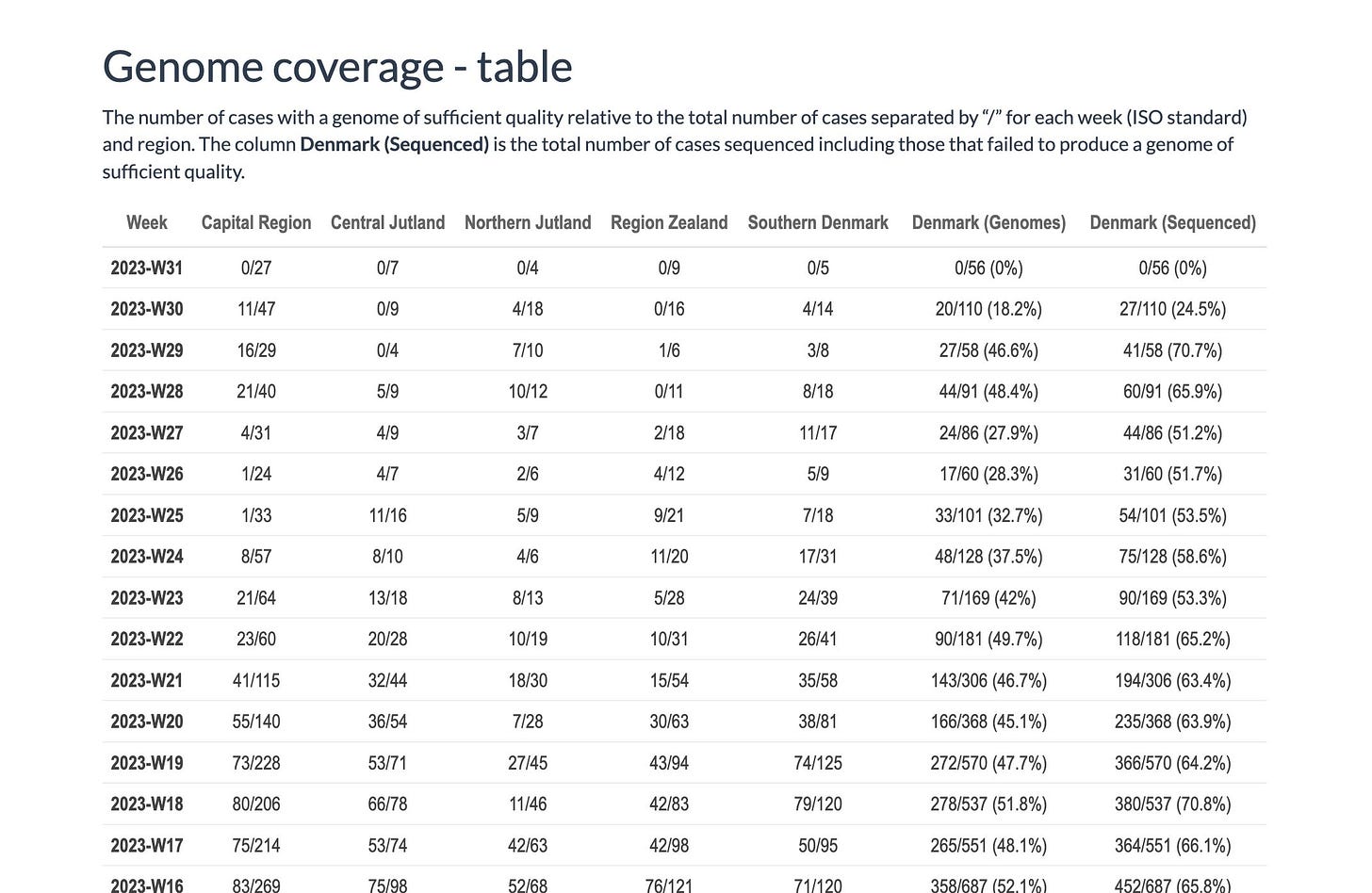
Just ten countries met an absolutely dismal threshold of submitting at least 10 sequenced positive test results over a two-week span. Based on that BA.2.75 is dominant in Europe with XBB.1.5 and one of its sub-variants trailing just behind. Basically, we don’t have a clue about the actual coronavirus spread and the variants involved in Europe anymore.
“A precise overview of variant distribution as well as early detection of newly circulating variants is difficult due to reduced sequencing volumes and a lower number of countries reporting data on SARS-CoV-2 sequencing or genotyping.”
🇩🇰
The Statens Serum Institute said it had not found any new cases of the BA.2.86 variant that is causing concern internationally. It said on Tuesday that out of the latest batch of 53 sequenced positive test results, there were no hits for the new variant. So far Denmark has confirmed three infections from the new strain. More data is expected to arrive on Friday.
Keep in mind that Danish authorities are not testing in any great numbers and of what minimal testing is being done a fraction of those are undergoing genome sequencing. For example, the first two infections confirmed to be the new variant at the end of July were from a batch of just 41 sequenced results. According to the SSI, there wasn’t a single positive test that was sequenced in the first week of August.
So far, BA.2.86 cases have been confirmed in Denmark, Israel, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the United States. While wastewater surveillance has also picked up the variant in Switzerland and Thailand.
-
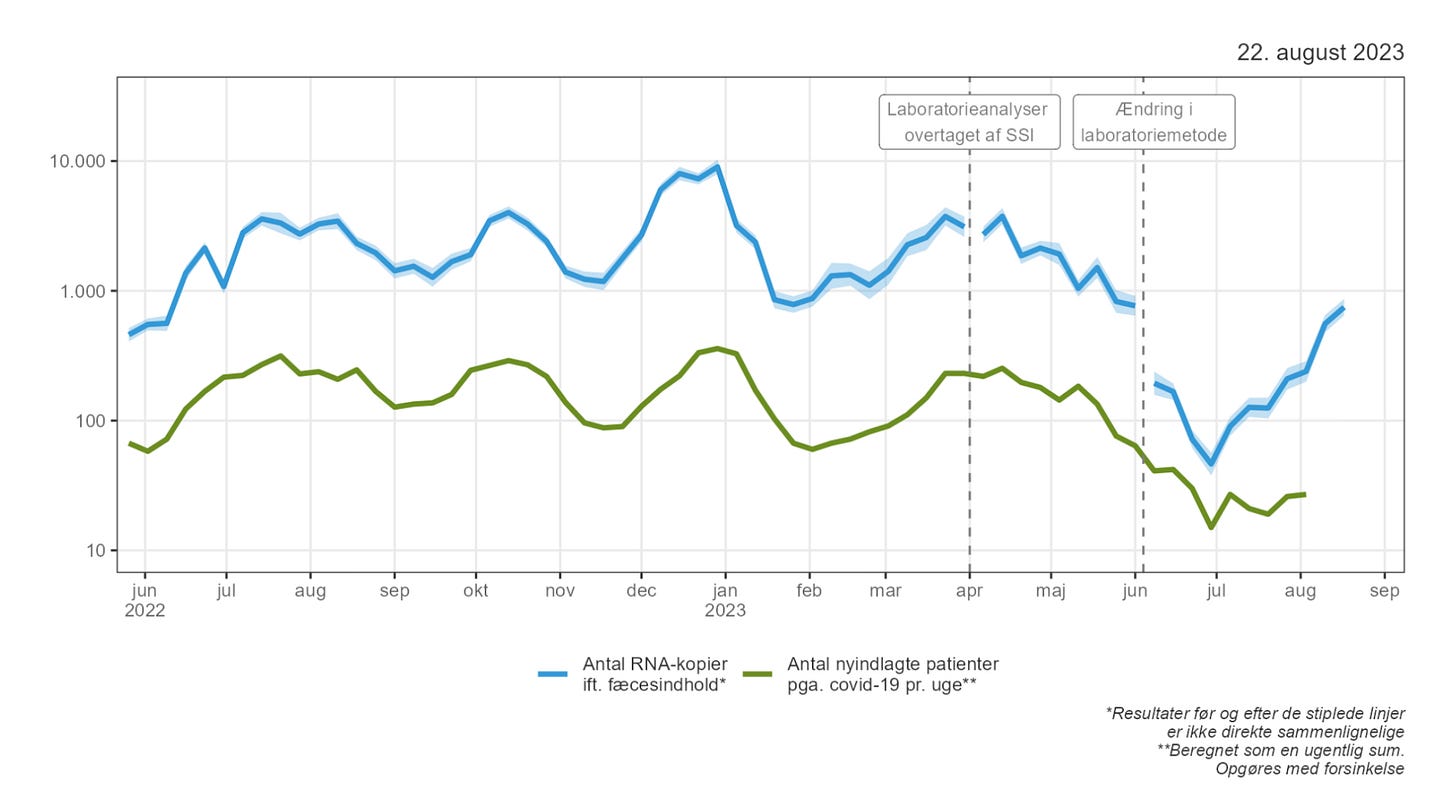
In the latest results from wastewater surveillance in Denmark, released on Tuesday, the Statens Serum Institute noted a “very strong increase” in coronavirus activity. It says levels now coincide with what we were seeing last April and May.
-
It seems like wild animals, for the most part, took advantage of the COVID lockdowns. An international study used GPS trackers on 43 different species to study their behavior during the pandemic lockdowns. Aarhus University in Denmark took part in the study. It found that in places with strict lockdowns at the height of the pandemic, animals took advantage of the lack of people and cars and expanded their territory in search of food.
Ecoscience Professor Peter Sunde spoke to DR
“On a daily basis, all mammals have to find resources to sustain life, but the figures show that the presence of cars and people stresses them and limits their movements to small areas empty of people.”
However, here in Denmark where people escaped COVID fears by flocking to nature areas there was probably the opposite effect on wildlife.
“The effect on wildlife has most likely been the opposite in Denmark. More people in nature have pressured the animals even more than usual.”
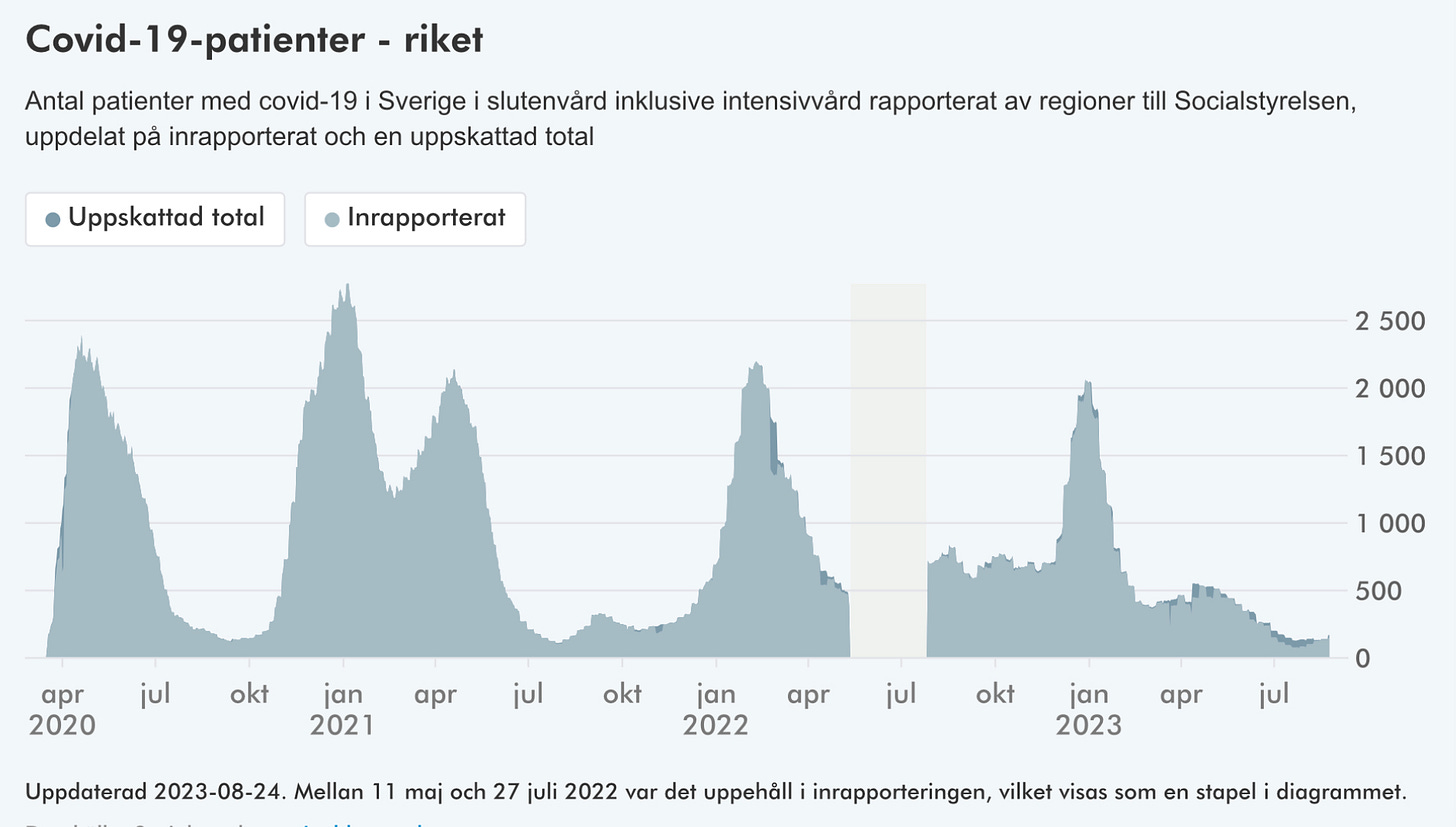
🇸🇪
In Sweden, COVID hospitalizations (151) have increased slightly (+15) while ICU numbers (1) dropped (-3).
-
A new study from Sweden’s Gothenburg University has directly linked the risk of severe infections with a person’s occupation. The study examined over half a million infection cases and then cross-referenced the most severe infections requiring hospitalization with the person’s job.
People working as a bus or tram driver were found to have had an increased risk of suffering from a severe COVID infection (98% increased risk). Other occupants at high risk included staff at after-school clubs (72% increased risk), registered nurses (68%), teachers, and preschool childcare workers (both 60%).
Professor of General Medicine at Sahlgrenska Academy, the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Gothenburg, Maria Åberg:
“When looking at specific occupations, interesting gender differences emerge. Among women, there are increased risks for specialist doctors, nurses, midwives and preschool staff. Male occupations that carry higher risk include bus and tram drivers and security guards. This also reflects the fact that we have a gender-segregated labour market.”
Åberg concludes that vaccination efforts need to be focused on staff in high-risk occupations with inoculations administered at work in order to reduce the infection risk.
You can read the study in full HERE.
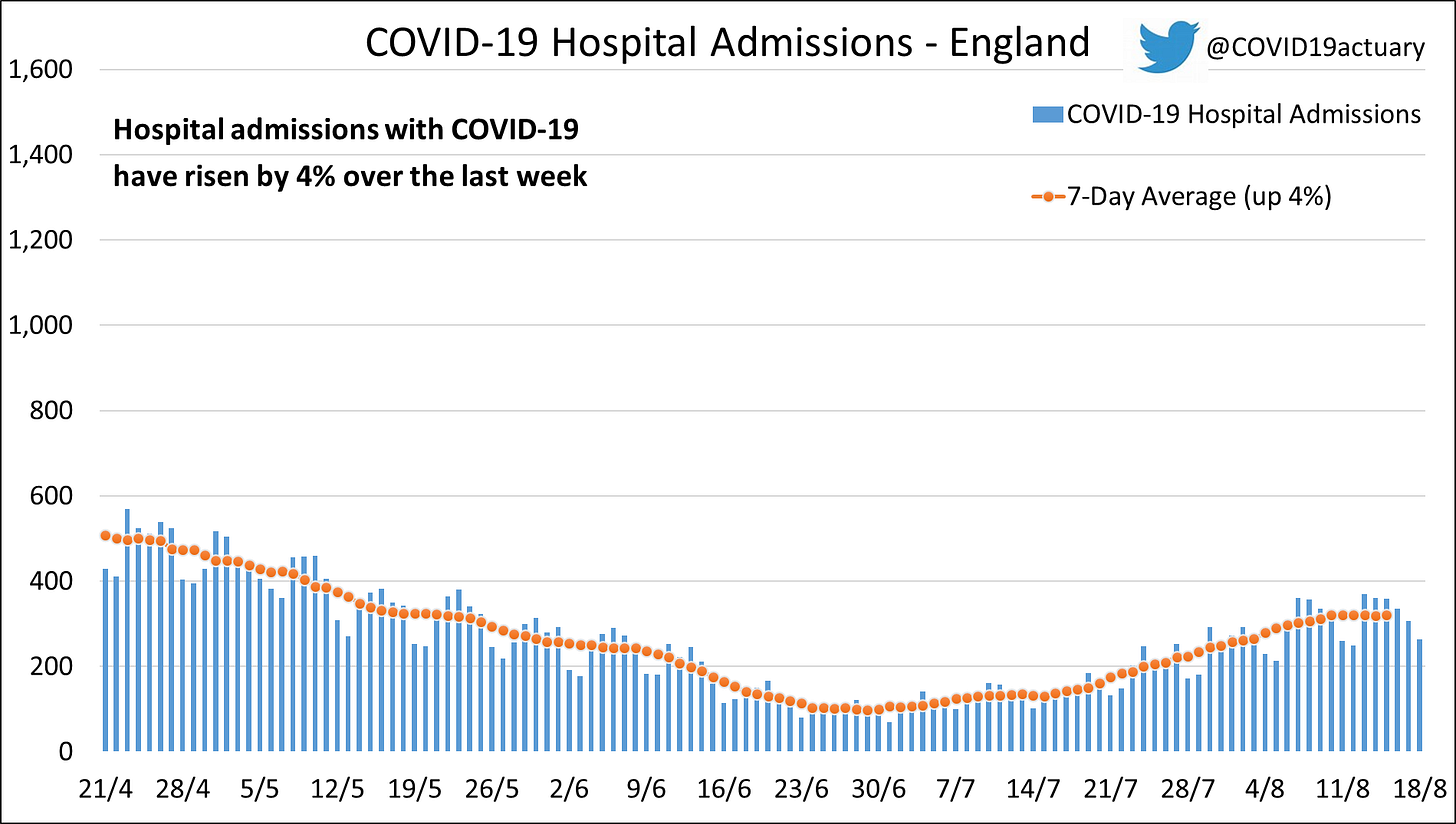
🇬🇧
According to the COVID Actuaries Response Group coronavirus hospitalizations in the United Kingdom nudged upward in the last week as admissions increased by 4%. Notably, infection-related admissions rose by 31% in London.
Intensive care occupancy also rose by 10%.
The reinfection rate, or R0, in England is an estimated 1.03. Anything over 1 indicates degrees of a spreading epidemic.
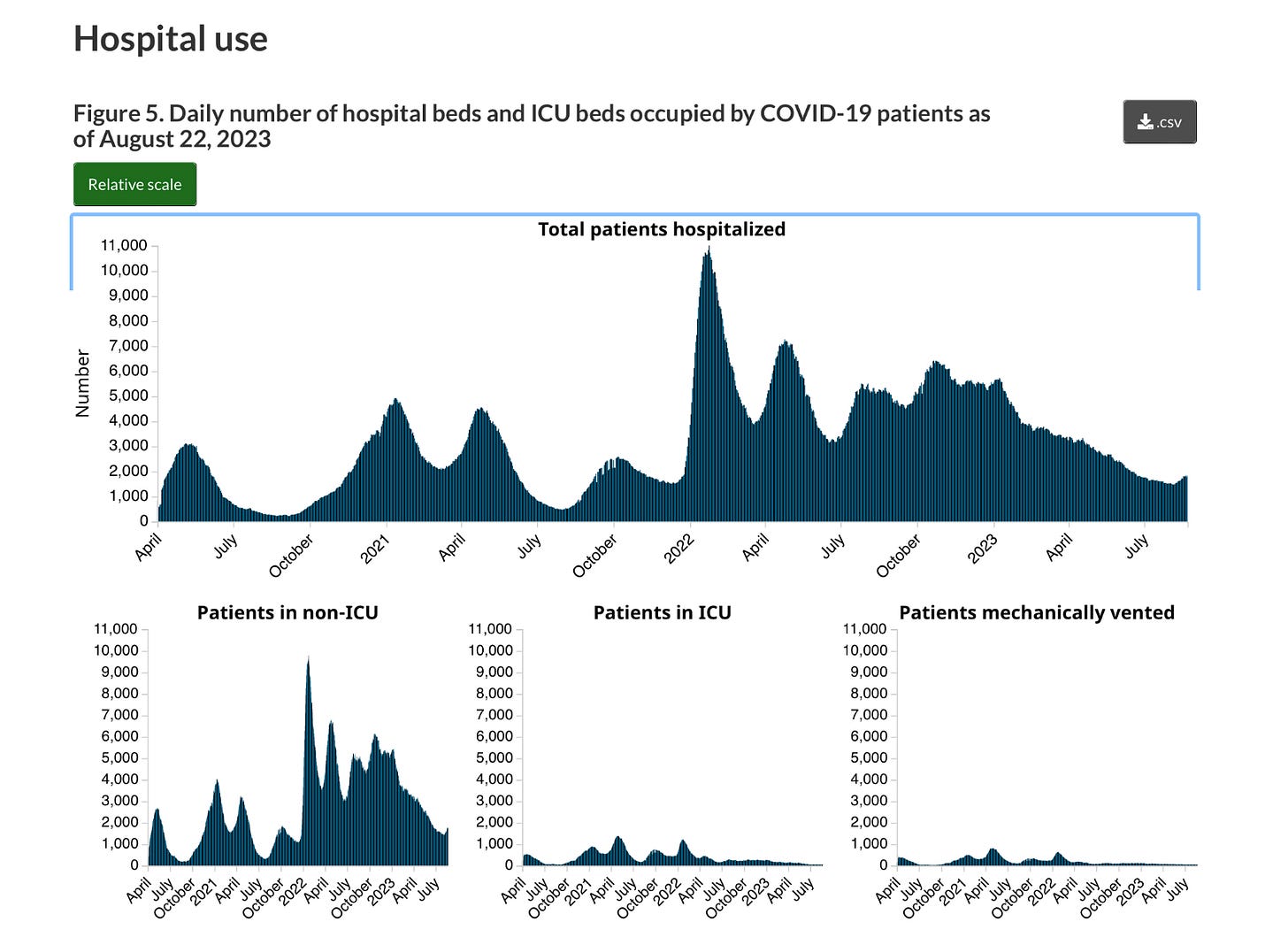
🇺🇸
The U.S. Centre for Disease Control and Prevention in its latest weekly assessment says both hospitalizations and deaths are increasing on the back of this latest COVID wave. In the week ending August 12, there were 12,613 new infection-related admissions (+21.6%) while deaths also rose (+8.3%). With over 1.1 million COVID fatalities and counting the United States has suffered by far the most virus fatalities of any nation on earth.
It is worth noting that some hospitals in the U.S. have already begun to reintroduce mask requirements.
-
This week the CDC published its first threat assessment for the new BA.2.86 variant. It concurs with the other risk assessments we have seen that the variant is probably a lot more active globally than we can see due to a lack of testing. It also notes that with cases popping up across multiple countries, there is plenty of evidence of international transmission. The CDC, like other health agencies, is also concerned about the sheer number of mutations in this strain.
It adds the jury is still out on whether the new strain is, or is not, more severe and to what degree it may, or may not, be able to dodge around immunity.
“It is too soon to know the real-world impacts on immunity. Nearly all of the U.S. population has antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 from vaccination, previous infection, or both, and it is likely that these antibodies will continue to provide some protection against severe disease from this variant. This is an area of ongoing scientific investigation.”
The CDC does not believe BA.2.86 is behind the increase in hospital admissions in the States. However it also cautions that as more evidence becomes available that assessment could change.
🇨🇦
Infection-related hospital admissions are still rising across Canada. In the week ending August 22, the total number of beds in use by a corona patient increased by 113 to 1,836. General admissions rose by 105 to 1,776 patients. Intensive care numbers crept upward by eight new patients to 60 in total. The only number bucking the trend was the number of severely infected people requiring a ventilator, which dropped by two to 53.
🦠
“Maybe you’ve forgotten about the SARS-CoV-2 infection but COVID did not forget about you. It’s still wreaking havoc in your body.”
A new study has found that people who suffered even mild coronavirus infections are at increased risk of a swath of health problems two years after being infected. People suffering from long-COVID, battling an array of symptoms long after recovering from an infection, are at risk of lung problems, fatigue, diabetes, and other lingering health challenges.
The study was published this week in the journal Nature Medicine. It attempts to shine a light on the plight of people who are battling long-COVID. The study concluded that the more severe the infection the higher the risk of debilitating after effects and that people with mild corona cases aren’t immune from the consequences either. Even they are at heightened risk of several dozen medical conditions years after infection.
The study in full can be found HERE.
-
COVID restrictions were excellent tools to limit infection spread, save lives, and buy time for vaccines to be developed. That is the conclusion of a new report from the United Kingdom’s National Science Academy.
Scientists at The Royal Society examined the use of COVID restrictions across several countries early in the pandemic. They determined that mask use, especially respirators, was very effective at limiting infection spread. Social distancing, travel restrictions, lockdowns, testing, and contact tracing were also successful at limiting coronavirus cases.
The Society does suggest that in the future more thought needs to be put into the impacts, cost, and socioeconomic effects of introducing restrictions. It also found that measures targeting schools certainly reduced virus spread but not nearly as much as restrictions introduced across the broader community.
The report does conclude that COVID restrictions had less impact once much more contagious variants appeared, like the Delta and Omicron variants. But it says COVID restrictions were an excellent method to save lives and buy time for life-saving vaccines to be developed. It recommends building on lessons learned, refining the restrictions, and utilizing them again in any future pandemic.
You can read the report in full HERE.
🇺🇦/ 🇷🇺 War
🇸🇪/ 🇹🇷 🇭🇺
Sweden will officially join NATO this fall. That is according to NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg who spoke to Sweden’s national broadcaster, SVT. However, Stoltenberg admitted he is careful not to pin it down to an exact date.
Hungary and Turkey have yet to ratify Sweden’s NATO application. Despite Turkey finally agreeing to support Sweden its parliament hasn’t met since it dissolved for last spring’s national elections. The Turkish parliament won’t sit until possibly October.
🇳🇴 🇺🇦
Norway will help upgrade Ukraine’s Air Force. The Norwegian Ministry of Defense said on Thursday that it will donate F-16 fighter jets to Ukraine. It does not specify an exact number but reports in Norwegian media peg the number of planes to be between 12 and 16.
Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre:
“We are planning to donate Norwegian F-16 fighter jets to Ukraine, and will provide further details about the donation, numbers and time frame for delivery, in due course.”
Norway says it will donate the jets in close cooperation with its allies. Denmark and the Netherlands have already pledged to donate 61 F-16s between them.
Minister of Defence Bjørn Arild Gram:
“We will continue our dialogue with the US and other close allies on the development of a modern air defense system in Ukraine. Norway has provided substantial military support to Ukraine and we will continue to do so. The donation of these F-16 jets will significantly strengthen Ukraine’s military capabilities.”
-
Norway also announced Thursday that is donating an unspecified number of IRIS-T anti-aircraft missiles. The Norwegian military says this will help save lives by preventing Russia from controlling the air space above Ukraine.
The missiles will be paired with launch systems supplied by Sweden.
Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre.
“Ukraine has received extensive donations of air defense from Western countries in the past, but the need is enormous. Norway will continue to support Ukraine in its struggle to defend itself against Russian forces. We will therefore now donate anti-aircraft missiles. This is one of the largest Norwegian donations of military material to Ukraine to date.”
Norway is also sending mobile de-mining kits along with explosive charges designed to clear corridors through Russian minefields. It was recently reported that Ukraine is now the most heavily mined country on earth.
🇸🇪 🇺🇦
Sweden’s economic woes may be one factor as donations to Ukraine dry up in the Scandinavian country. According to a report from Swedish Radio's P4 Värmland private donations to help war victims in Ukraine have absolutely fallen off of a cliff. UNICEF Sweden says it has collected less than 10% of the donation by April of this year than it did by April of last year.
🇩🇪 🇺🇦
Germany is sending more weapons to Ukraine. The German government announced on Thursday it will send Ukraine Patriot missiles, eight drone detection systems, 40 RQ-35 HEIDRUN reconnaissance drones, and 31 million rounds of small arms ammunition.
🇨🇦/ 🇷🇺
The Canadian Government has levied more sanctions against Russia. The latest measures target four individuals and 29 entities all with ties to Russia’s military-industrial complex and to the country’s financial and nuclear sectors. They include a Russian Colonel who is associated with the brigade implicated in the shooting down of Malaysia Airlines flight MH17 in 2014.
The companies targeted with sanctions develop equipment, technology, and weapons used in Russia’s aviation, marine, and nuclear sectors. One, Promtekhnologiya LLC, supplied weapons for the notorious militia group Wagner.
The sanctions also target financial institutions already sanctioned by Canada’s G7 allies.
Foreign Affairs Minister Mélanie Joly:
“Canada continues to condemn in the strongest possible terms Russia’s illegal war of aggression against Ukraine. We will continue to work with our partners, including the G7, to undermine Russia’s ability to conduct its military aggression against Ukraine and to impose further costs on those who support the Russian regime.”
🇩🇰 😆
Beginning next year parents in Copenhagen and daycare workers will have to dispose of children’s used diapers in special recycling bins. The city will send out some 4,800 of the special containers to apartment buildings and daycares. The city’s Environmental Administration calculates that adopting the diaper disposal scheme will allow for 3,340 tonnes of diaper waste to be recycled every year.
However, there is a little flaw in the plan. At the moment there isn’t a company in any of the Scandinavian countries or anywhere near them that can recycle diaper waste. This means fun-smelling shipments of dirty diapers will have to be sent from Copenhagen to recycling facilities in places like the Netherlands, Italy, or perhaps even as far away as Wales.
The city says each year about 46 million dirty diapers end up in Copenhagen’s garbage bins.




On the whole diaper recycling thing , so much waste ( No pun intended). We used cloth diapers. Better all around. Daycares need to rethink using cloth diapers . 😊